The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is experiencing the largest outbreak of viral pox on record, with tens of thousands of people infected as of June. In December 2022, the government declared it an epidemic.
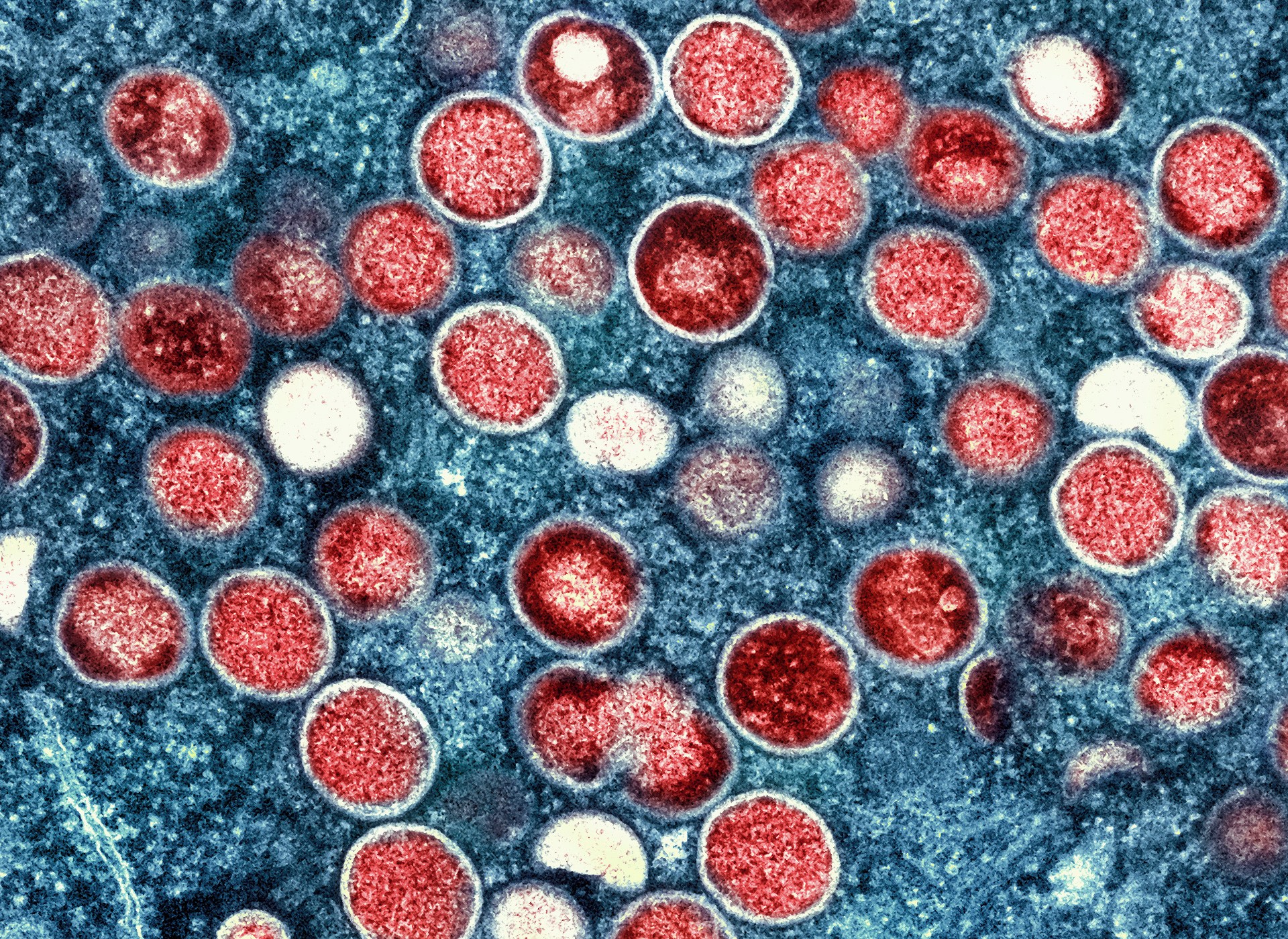
Empox disease, formerly known as monkeypox, is caused by a monkey virus, and is typically zoonotic – that is, it can be transmitted from animals to humans.
The virus is endemic in densely forested areas of central and western Africa and is closely related to the now extinct smallpox virus. In severe cases, empox can be fatal, the main symptoms are itching all over the body and fever. Vaccines can prevent infection.
Reports in the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Republic of the Republic of the Republic of the Republic of the Republic REPUBLIC REPUBLIC REPUBLIC REPUBLIC REPUBLIC RESEARCH
Here’s what we know about the outbreak:
When did the mpox epidemic begin?
The outbreak began in May 2022 in the country’s eastern Kwango province. However, it has since spread to 22 of the Democratic Republic of Congo’s 26 states, including the capital Kinshasa.
Distribution is still concentrated in the east, however the highest prevalence is recorded in Kamituga, a mining town in eastern South Kivu province. Doctors found a new type of virus in the city.
As of 2022, more than 21,000 cases and more than 1,000 deaths have been reported by the World Health Organization (WHO). A total of 14,626 cases and 654 deaths were recorded in 2023.
This year alone, 7,851 cases were reported by the end of May and 384 people died. Most of those infected are children under the age of five (39 percent). About two-thirds (62 percent) of those who die from the disease are children.
The country’s Equator, South Ubangi, Sankuru and South Kivu provinces are among the worst affected.
How many types of mpox are there and how deadly are they?
There have always been two types of mpox known as clades.
Clade 2 is less lethal. It was the type that spread in the 2022 pandemic, first recorded in London in 2022 and reaching 111 countries in Europe, South and North America, Africa, the Middle East, Asia and Oceania. More than 99 percent of people infected with this outbreak survive because the outbreak is less lethal. Rich countries affected by the epidemic have also been able to stockpile vaccines and antiviral drugs for treatment.
Clade 1 classification, however, is more severe, and can kill up to one-tenth of those infected. It is clade 1 in DRC, and it is causing the current outbreak.
This layer of the virus is typically spread through casual physical contact. However, experts say that the infection is mostly spread through sexual contact.
Dr. Jean Bsimwa Nachega, a professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, said this is especially true in Kamitouga, a hot area with many sex workers.
Kamituga is where the new clade 1 category was discovered in September 2023.
This is a “huge development,” said Dr. Nachega, citing the vulnerability of sex workers, who, in addition to being economically disadvantaged and lacking health care, are more likely to have compromised immune systems than the rest of the population. Like HIV.
“Unlike historical animal-to-human transmission, human-to-human sexual transmission, particularly among high-risk groups such as sex workers, adds a new challenge to controlling the virus,” he said.
The World Health Organization says it is unclear if this difference is more contagious or leads to more serious illness.
Doctors interviewed by The Associated Press said the new variant is being approached differently. Mpox lesions usually appear on the face, arms, chest, and legs, and are clearly visible on an infected person. In this case, however, the reported wounds are mostly found on the genitals, experts said, which makes it very difficult to track and diagnose cases.
In the reports from the Democratic Republic of the Republic of Korea, there were no cases of sexual transmission of clade I virus. Cases in the country reported since the 1970s are understood to be mainly due to casual direct contact with infected people or animals.
What are the main obstacles that the authorities face?
Democratic Republic Democratic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic REPUBLIC REPUBLIC REPUBLIC REPUBLIC REPUBLIC REPUBLIC REPUBLIC The Republic of Republic of Republic of Republic of Republic of Republic of Republic of Republic has only two testing laboratories in Kinshasa and Goma, and only 18 percent of the reported cases have been tested in the laboratory.
The World Health Organization says there are insufficient medical equipment and no vaccine in the country. Tecovirmat is an antiviral drug approved for smallpox in the Democratic Republic of the Republic of Korea Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic Republic According to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Vaccines could help reduce the spread and were critical to preventing epidemics in developed countries such as the United Kingdom and the United States by 2022. But the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic Democratic Republic Democratic Republic Democratic Republic Democratic Republic Democratic Republic Democratic Republic Democratic Republic Democratic Republic Democratic Republic DC The country’s health minister has authorized doctors in high-risk areas to administer vaccines. The Democratic Republic of Congo is in talks with countries including Japan to buy more vaccines, officials said.
Public awareness of mpox is limited, making self-reporting and detection difficult. Some patients have withdrawn to buy food or continue their professional activities, experts said.
The fact that the disease can now be sexually transmitted brings an additional layer of stigma, a problem that plagued health care workers during the initial spread of HIV/AIDS, experts have pointed out. Experts say there is a risk of “silent transmission” if people don’t come forward.
What are the risks for other African countries?
The eastern region of the Democratic Republic of Congo, which borders Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda and Tanzania, is also a transit point where people regularly enter and leave, increasing the possibility of transmission to other countries. The Democratic Republic of the Congo is bordered by the Democratic Republic of Zambia and Angola in the south, while the western and northern regions are bordered by the Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, and South Sudan.
As the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic Republic of the Republic of the Republic of the Republic of the Republic of the Republic of the Republic of
“Infectious diseases do not respect borders. As seen with Covid-19, outbreaks in one region can quickly spread to other parts of the world. Although the current outbreak of mpox appears to be confined to one part of the Democratic Republic of Congo, people on the continent should be vigilant, he said.
So far, 19 cases have been found in the Republic of the Congo, spread from the Democratic Republic of the Congo – although this has not been confirmed. In April, authorities there declared a public emergency.
Also, 23 clade 2 viruses were reported in Cameroon between January and April this year. South Africa has recorded five clade 2 cases in an outbreak between January and May, although the World Health Organization says there may be more unreported cases.
These cases are not directly related to the outbreak of the Democratic Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. There is frequent commercial travel to South Africa and the Democratic Republic of Congo, but some experts believe the cases are linked to a global clade 2 outbreak in 2022.